This exploration is for early and middle grades, as the colored smileys show. You can learn about the legend of the Capitoline Geese with your kids from 6 to 13!



The Capitoline Geese exploration is from Ancient Rome. Layers of Learning has fun printables in every unit of this family-friendly curriculum. Learn more about Layers of Learning.
When we think of Rome it is usually of the mighty years of the empire. But in the earlier centuries, Rome was attacked frequently by foreign armies and had to struggle for existence. The story of the Capitoline Geese is one of those struggles.
Step 1: Library Research
Before you begin exploring, read a book or two about ancient Rome. Here are some suggestions, but if you can’t find these, look for books at your library about Rome, famous Romans, and Roman Republic. The colored smilies above each book tell you what age level they’re recommended for.
As Amazon affiliates, the recommended books and products below kick back a tiny percentage of your purchase to us. It doesn’t affect your cost and it helps us run our website. We thank you!

Brave Cloelia
by Jane Curry

Step 2: Capitoline Geese Exploration
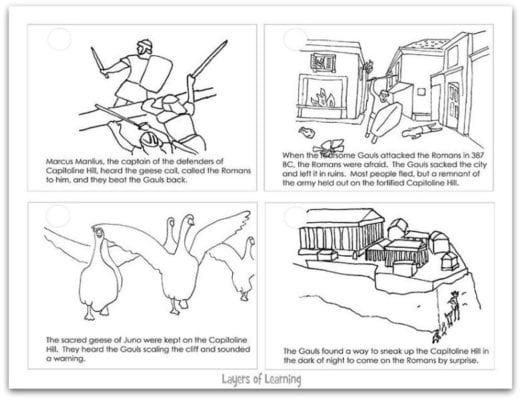
You will need the printable story of the Capitoline Geese, crayons or colored pencils, scissors, and a stapler.
On the printable, the parts of the story are out of order. There are circles on the corner of each page. As you read or tell the story, kids should write the order of the panels in the circles. Then they can color and cut out the pages to make a book.

Here is a Capitoline Geese Legend cover for the book as well. There are two covers on each of these sheets. We printed our covers on colored paper. Staple all the pages together along the spine.
The Legend of the Capitoline Geese
There is a legend that in the year 387 BC, the Gauls crossed the Alps and entered the Italian Peninsula. They came searching for new land for their people and of course the wealth of the fertile north of Italy. By that year the Roman Republic was well established and the Romans had conquered or made treaties with enough of their neighbors that they were growing powerful.
The Gauls heard about the power and wealth of Rome and so they wanted it for themselves. The Romans were warned of the advance of these barbarians from the north and went out to do battle. The Gauls were more terrible than the Romans could have imagined. Many of them fought naked and their bodies were painted and tattooed with strange designs, their hair and their visages were twisted and cruel. Their battle cries were horrifying. Their weapons were wicked and they wielded them with an ease that no Roman could match. The Roman soldiers, every one, turned tail and ran back through the city gates, leaving the gates wide open in their panic.
That would have been the end of Rome then and there except that Gauls were leery that the Romans had left the gate open as a trap. And so the Gauls waited for three days. During those three days the citizens of the city were able to flee to other parts and the remaining soldiers were able to entrench themselves on the Capitoline Hill. At length, the Gauls decided the Romans really were cowards and they entered the city, sacking, looting, and burning as they went. But they could not breach the defenses of the Capitoline Hill.
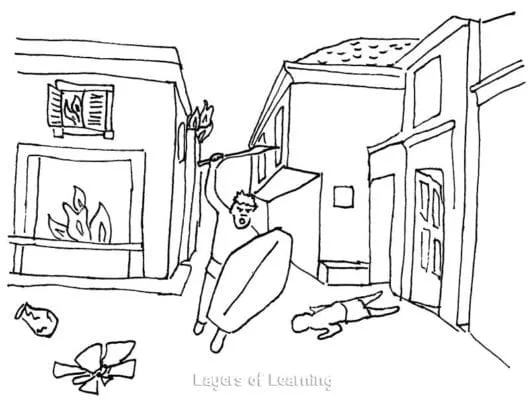

Then one night, one of the Gaulish spies said he had found a way. They could climb up the back of the hill, up a steep cliff by means of handholds. If they climbed the hill quietly they could gather a strong enough force to battle their way to the gate and let their fellows in.
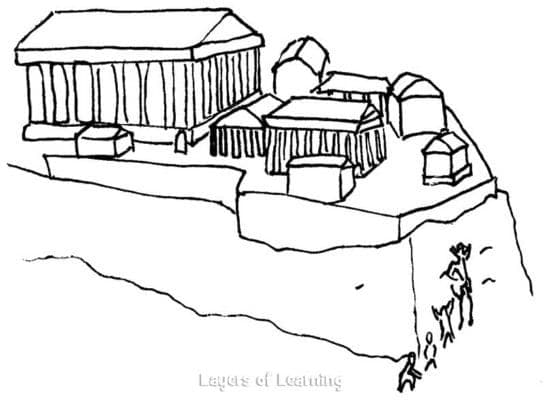
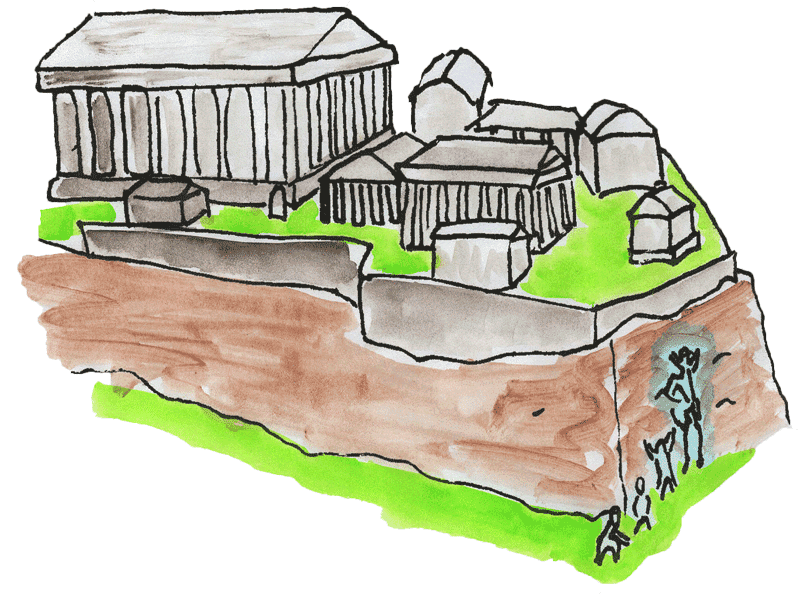
Now, the Capitoline Hill was the site of the temple of Juno. Since geese were sacred to Juno, the priests kept a flock of geese on the hill. And even though the siege had been going on for many weeks and the soldiers were on short rations they left the sacred geese alone.
It is lucky that they did for on the night the Gauls decided to scale the back of the Capitoline the sentries had fallen asleep on duty and the dogs were silently snoring. But the geese heard the invaders as they scaled the hill and they sent up such a cackling and honking and flapping of wings that Captain Marcus Manlius woke abruptly, grabbed up his sword, and rushed out to the parapet, calling his men as he ran. He was first to the wall, but others soon appeared at his right and at his left. They threw the Gauls back from the cliff.
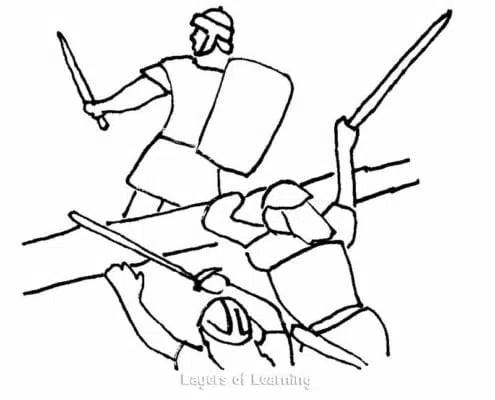
The siege continued on for a few more weeks but the Gauls grew bored and decided to make a treaty. The Romans were able to buy peace at a great cost. But Rome endured and one day grew to be a great empire.

The sacred geese of Juno were honored every year after in a processional through the city commemorating their defense of the city of Rome.
Step 3: Show What You Know
After you complete the story books, have the kids tell the story back to you without reading it. They can show off their coloring in the books too. Telling back stories is great practice for sharpening the memory and summarizing or narrating in the child’s own words. This skill will be used whenever the child has to write a report or paper where they need to summarize information in their own words.
Additional Layers
Additional Layers are extra activities you can do or tangents you can take off on. You will find them in the sidebars of each Layers of Learning unit. They are optional, so just choose what interests you.
Writer’s Notebook
This activity has kids put the story in order. This is a good time to practice story order and to talk about how stories have beginnings, middles, and endings.
Rewrite the story of the Capitoline Geese from the point of view of a character in the story. It could be a Gaulish soldier, a Roman soldier, or one of the geese.
Deep Thoughts
The city of Rome was built on seven hills. The Capitoline Hill was where the rich people lived and where the public buildings, like temples and the senate chambers, were located. It was no mistake that that was the part of the city the Roman soldiers were ordered to protect. During the siege, the ordinary citizens lost everything. When it was all over and they came back home, the senate carried on like nothing had happened, taxing the people as before. This was obviously a great hardship and many now destitute citizens ended up in debtors prison or begging in the streets. Marcus Manilus, who had gained notoriety for his defense of the city, spoke up, condemning the actions of the senate. They had him killed as a traitor for stating his opinion, but he did start a movement of reforms that gave more power to the common people. Discuss this attitude of the rich senators toward the rest of the people. Is this typical among all governments or unique to Rome? How can the common people defend themselves from their own government?
Get a Free Unit
Choose between the first unit in each Layers of Learning subject to try for free when you sign up for the newsletter.
We never spam and you can cancel your subscription at any time.